Overview
One of the key concepts in electronics is the printed circuit board or PCB. It's so fundamental that people often forget to explain what a PCB is. This tutorial will breakdown what makes up a PCB and some of the common terms used in the PCB world.
Over the next few pages, we'll discuss the composition of a printed circuit board, cover some terminology, a look at methods of assembly, and discuss briefly the design process behind creating a new PCB.
What's a PCB?
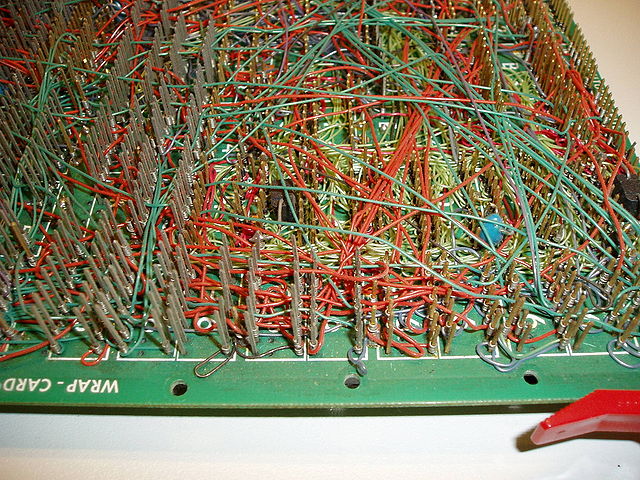
Printed circuit board is the most common name but may also be called "printed wiring boards" or "printed wiring cards". Before the advent of the PCB circuits were constructed through a laborious process of point-to-point wiring. This led to frequent failures at wire junctions and short circuits when wire insulation began to age and crack.
A significant advance was the development of wire wrapping, where a small gauge wire is literally wrapped around a post at each connection point, creating a gas-tight connection that is highly durable and easily changeable.
As electronics moved from vacuum tubes and relays to silicon and integrated circuits, the size and cost of electronic components began to decrease. Electronics became more prevalent in consumer goods, and the pressure to reduce the size and manufacturing costs of electronic products drove manufacturers to look for better solutions. Thus was born the PCB.
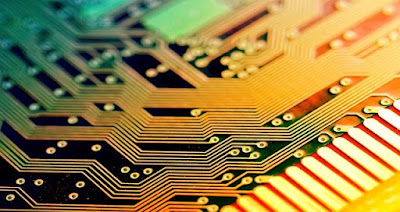
PCB is an acronym for the printed circuit board. It is a board that has lines and pads that connect various points together. In the picture above, there are traces that electrically connect the various connectors and components to each other. A PCB allows signals and power to be routed between physical devices. Solder is the metal that makes the electrical connections between the surface of the PCB and the electronic components. Being metal, the solder also serves as a strong mechanical adhesive.
Composition
A PCB is sort of like a layer cake or lasagna- there are alternating layers of Continue ...
Unless your PCB is designed correctly in the first place, you are going to run into issues sooner or later.
Designing a PCB for one of today's products can be very complex, but this aspect of things is often overlooked. Instead, the focus falls upon the more "interesting" aspects of the product, like the FPGAs or MCUs. The fact remains, however, that unless the board is designed correctly in the first place, you are going to run into issues sooner or later.
Technological advances have ensured that Printed Circuit Boards cannot only perform complex functions they can also be produced inexpensively. This is the exact reason why PCBs are an integral part of so many devices. However, the quality of the device is directly proportional to the quality of the PCB used. PCB failure can, therefore, have debilitating consequences wherein entire systems can fail. It is therefore extremely important to stick to some quality measures in the PCB design and manufacturing process.